Peptic Ulcer is any discontinuity or erosion of the GI
mucosa. Various factors are involved in the mediation of ulcer and play direct
and indirect role in the ulceration. However esophageal ulceration is generally
kept in the separate category of GORD. This definition also exclude carcinoma
and lymphoma which may also cause ulceration and also exclude Crohn,s disease,
viral infections and amyloidosis. The prevalence of this disease is as common developed as in under developed countries, except the H Pylori mediated Ulcer, is more
prevalent in Under-Developed countries.
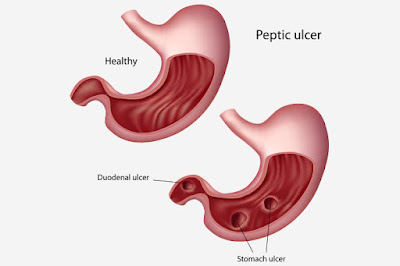 |
| Peptic Ulcer |
Pathogenesis
Pathogenesis of Peptic Ulcer ( Word used for both Gastric
and Duodenal ulcer) varies. Pathogenesis include factors like Halicobacter
Pylori, NSAIDS, Stress and other factors previously excluded form the
definition.
H Pylori
It is the most common cause of the Ulceration. About 80
Percent of Ulcers are due to this bacteria (one of the cancer causing
bacteria). The spread of this bacteria
is possible through oral-oral, oro-fecal and other means like bad sharing, food
sharing and congested areas. The pathogenesis cause by this bacteria is due to the
cytotoxins like Cag A and other associated enzymes including urease,
haemolysins, neuraminidase and fucosidase which digest the mucosal layer of the
GI tract. In addition Hyper-acidity caused by H Pylori is due to the mediation
on D cells decreasing D cell number which secrete Somatostatin. Somatostatin
has inhibitory effect on the gastrin. So Low D cell low somatostatins and High
level of Gastrin (Hypergastrinaemia) which leads toG receptor stimulation on parietal cells and also increase in Parietal
cell mass (HCl secreting Cells).
NSAIDS
NSAIDS mediated ulcer follow three pattern of pathogenesis,
including Superficial erosions, systemic effect due to COX inhibition and Hemorrhages
which may exacerbate the ulcers. Superficial erosions mainly defined by the
gastric acid mediate concentration of the weak acid like aspirin in the mucosal
cells where it block COX and also by
increasing adherence of leucocytes to mucosal endothelia cells. Along with
these one of the major effect is the low
production of systemic prostaglandin production.
Stress
Stress is also on of the common factors for GI ulceration. Among potential mediators, several known
behavioral risk factors for ulcers—smoking, alcohol abuse, and lack of sleep—have
clear relations with real-life stress and are known to weaken wound healing
through their effects on immune function, sleeplessness can also elevation of
cortisol level. A people under stress
may also have increased use of NSAIDS.
Low blood flow to the stomach is one of the proposed mechanism due to
which the mucosal secretion and synthesis decrease (one of the protective phenomenon
of GI tract). Delayed gastric emptying in stress and increased Acid secretion
are also included factors of stress. Similarly physiological stress as head
injury, spinal cord injury and others may also contribute to Ulcers erosions.
Idiopathic Ulcers
There are idiopathic tendencies of Ulcers. Confirmed by
genetic and twin studies. It may run in families. Idiopathic ulcers is also connected
with poor life style habits. However idiopathic ulcer is rare as compare to the
factors induced one.







Bohut he zbr10 effort....Jazakalllah
ReplyDeletekeep on doing the job
got lot of information by ths blog
ReplyDeleteprescription discount card online
Thank you Sir
ReplyDeleteNice information in this blog